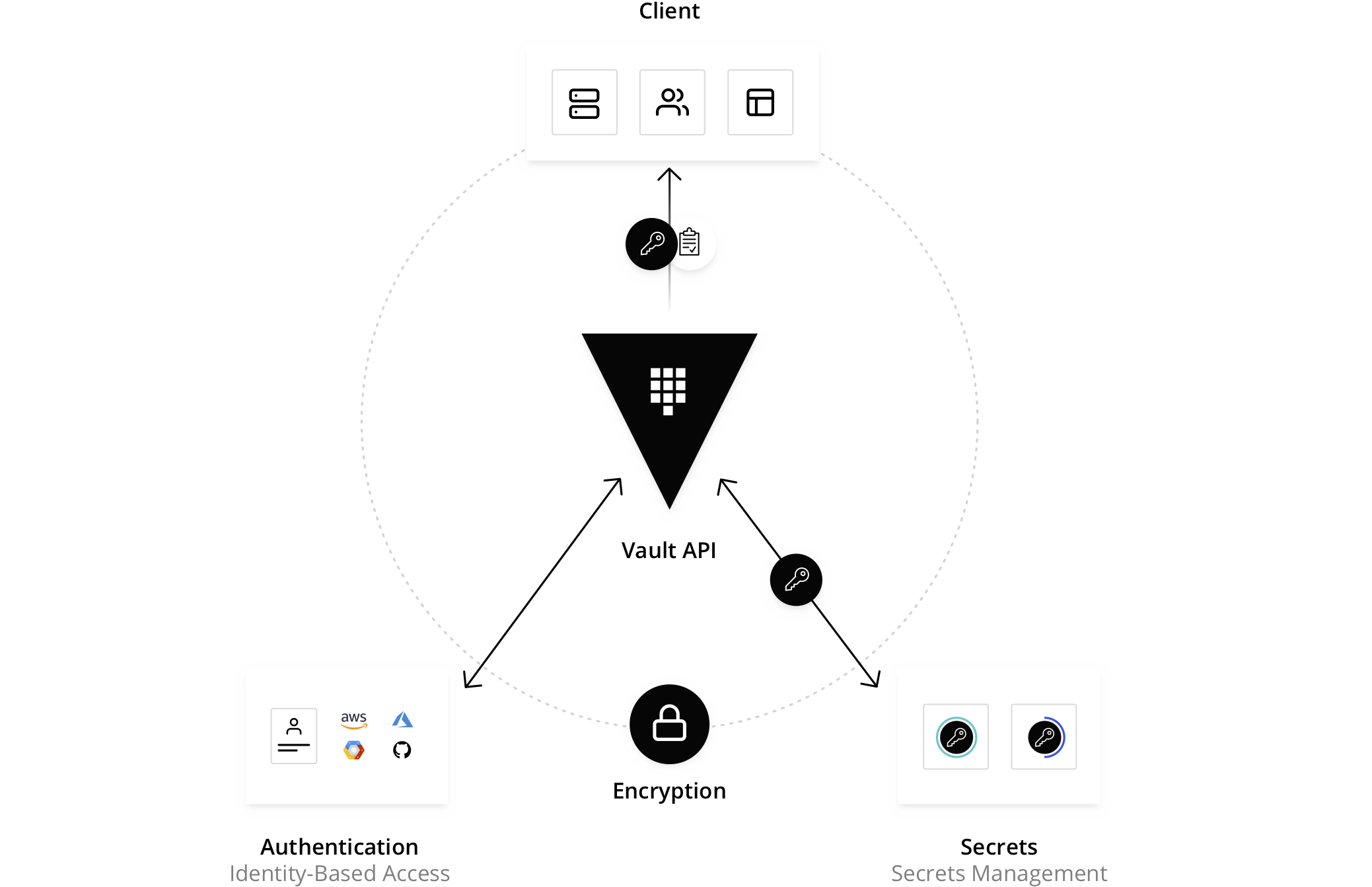
What is HashiCorp Vault?
HashiCorp Vault is a tool designed to address the challenges of managing and securing secrets in modern IT environments. Vault provides a secure, centralized system for storing and managing secrets, such as passwords, API keys, and TLS certificates. Vault supports a wide range of secret types and can be extended to support custom secrets as well.
Vault is designed with security in mind and provides several layers of protection for secrets, including encryption, access controls, and auditing. Vault also provides a flexible and extensible architecture that can be integrated with other tools and services in a modern IT environment.
Why Use HashiCorp Vault?
Security: Vault provides a secure, centralized system for managing secrets, with features such as encryption, access controls, and auditing
Efficiency: Vault enables organizations to manage secrets in a centralized and efficient manner, reducing the risk of human error and making it easier to enforce security policies.
Flexibility: Vault supports a wide range of secret types and can be extended to support custom secrets as well. Vault also provides a flexible architecture that can be integrated with other tools and services in a modern IT environment.
Compliance: Vault can help organizations comply with security and data protection regulations, such as PCI-DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR, by providing a secure and auditable system for managing secrets
How Does HashiCorp Vault Work?
Vault works by providing a secure and centralized system for storing and managing secrets. Secrets are stored in a Vault backend, which can be a local file system, a cloud-based storage service, or a distributed key-value store. Vault supports several backends, including Consul, etcd, and ZooKeeper.
Vault uses a flexible and extensible system of secret engines to manage different types of secrets. Secret engines can be enabled, configured, and managed through the Vault API or command-line interface. Vault supports several secret engines out-of-the-box, including key-value, database, and SSH engines, and can be extended to support custom engines as well.
Vault also provides several layers of security for secrets, including encryption, access controls, and auditing. Secrets are encrypted both in transit and at rest, and access to secrets is controlled through a system of policies and roles. Vault also provides detailed auditing and logging of all access to secrets.
What we do
1.Install and configure Vault
First, you need to install and configure Vault. You can follow the official documentation for your operating system to install Vault.
Once installed, you can start Vault in development mode by running the following command:
vault server -dev
This will start Vault in development mode with a root token and a default unseal key. You can use the root token to authenticate with Vault and enable secret engines,
Note: do not use root token in production env.
2.Enable a KV secret engine
Next, you need to enable a secret engine in Vault. Secret engines are plugins that provide a way to generate and store secrets. For this example, enable the KV secret engine, which provides a simple key-value store for secrets.
To enable the KV secret engine, run the following command:
vault secrets enable -version=2 -path=secret kv
3.Store a secret in KV Secret Engine
Now that the secret engine is enabled, you can store a secret. For this example, we will create a Auth token from Third-Party service and store it in Vault. Create below file and run the following command:
secrets.json
{
"AUTH_TOKEN":"#fhikr@1d@@v2jk96scwq7rbhkc3!l3jl53m7jdkmqrp9*y86$"
}
Run the following command to store secret:
vault kv put -mount=secret project/thirdparty/dev @secrets.json
4.Create a GitHub Actions workflow
Next, you need to create a GitHub Actions workflow that retrieves the secret from Vault and uses it in the workflow.
Create a new file in your repository at the following path:
.github/workflows/main.yml
Add the following content to the file:
steps:
# ...
- name: Import Secrets
id: import-secrets
uses: hashicorp/vault-action@v2.4.0
with:
url: https://vault.domain.com:8200
token: ${{ secrets.VAULT_TOKEN }}
secrets: |
project/thirdparty/dev auth_token | AUTH_TOKEN ;
This workflow performs authentication to vault and retretive the secret store in project/thirdparty/dev path in KV Secret Engine.
5.Set up a Vault token for Github Actions
To authenticate with Vault in the workflow, you need to set up a Vault token as a secret in the repository.
Create a policy in vault to provide permissions to read token from path.
policy.hcl
path "secret/project/thirdparty/*"
{
capabilities = [ "read","list"]
}
Path value depends on requriment and usecases,best pratices to provide only permissions to path required.
Write a policy in vault cluster using below command:
vault policy write gh-actions policy.hcl
Generate token with above policy using below command:
vault token create -field=token -policy gh-actions
Token generated from above step should be configured in github actions secret as VAULT_TOKEN variable.
TuneTTL and MAX_TTL as per your requirments
Summary
Vault is a powerful tool that can help you to manage your secrets and secure your DevOps pipeline. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can install and configure Vault, enable a secret engine, create a secret, and integrate it into a GitHub Actions workflow. By using Vault to store and manage your secrets, you can ensure that they are kept secure and only accessed by authorized users and workflows, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches. This can help you to maintain a robust and secure DevOps pipeline, while also streamlining your development and deployment processes. With Vault, you can take control of your secrets and build a more secure and efficient development workflow.